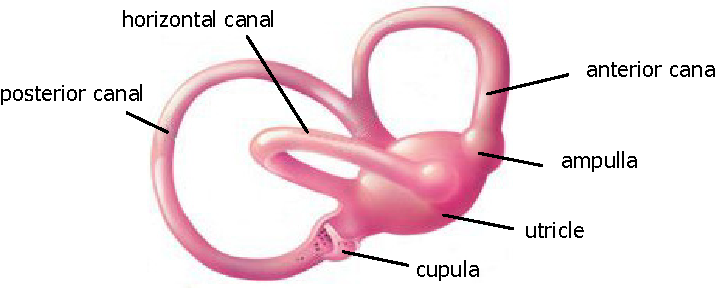
A sixth sense? Guess again. Researchers have discovered that humans have between nine and 21 senses (sight, taste, touch, pressure, itch, thermoception, sound, smell, proprioception, tension sensors, nociception, equilibrioception, stretch receptors, chemoreceptors, thirst, hunger, magnetoception, time. Generally, common knowledge is that humans have five senses: sight, touch, taste, smell, and sound. Our very existence is defined by anything and everything we experience through those five senses. But today, science has come to a conclusion that there are much more than just five senses.